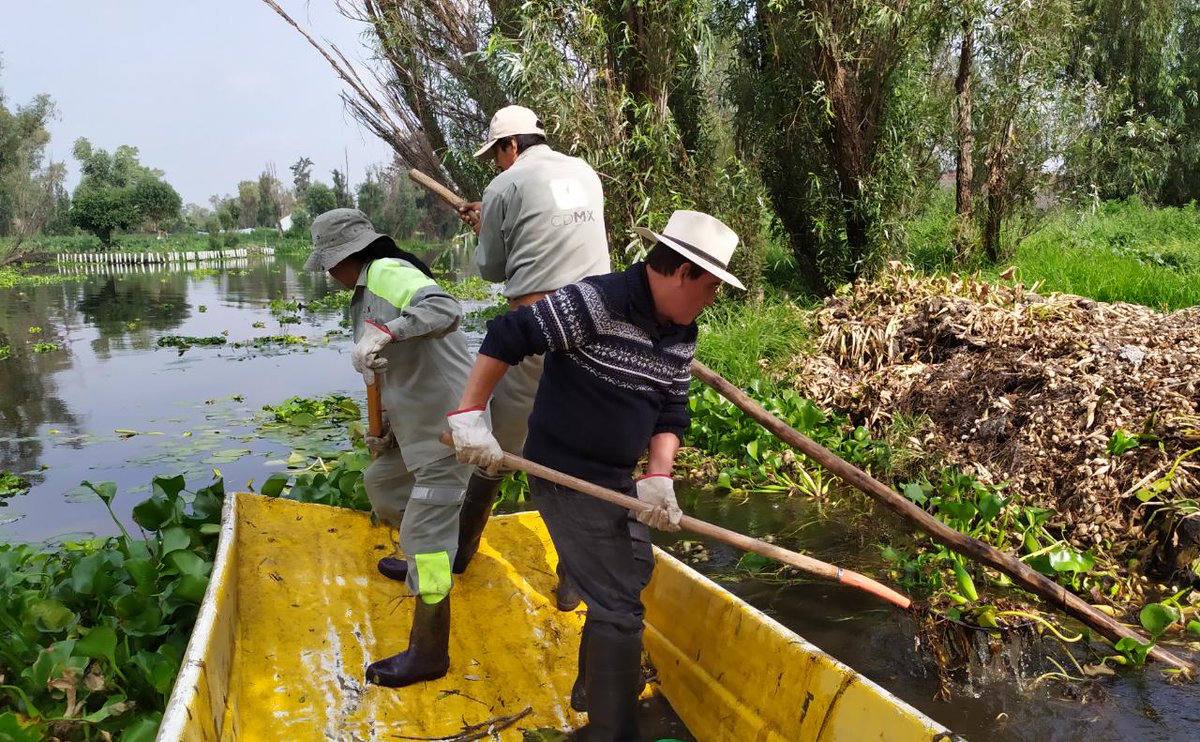
The water lily in Xochimilco looks very cool, of course, but over time it has become a weed for that ecosystem.

A characteristic postcard: a landscape of green plants and live flowers floating on the water, next to the water lily in Xochimilco. It looks very cool, of course.

However, this plant – brought for its beauty from the Amazon – has become a noxious weed. Its removal costs hundreds of thousands of pesos per hectare and covers 40,000 in the country.
A group of researchers came up with a solution: through a biorefinery in CDMX, they convert this flower into enzymes, nanocrystals, compost, and even biogas and bioethanol.
The team has been working since 2009 on the project for the exploitation and profitability of the use of this plant and is part of the Department of Biotechnology of the UAM Iztapalapa. It is headed by Dr. Ernesto Favela Torres, professor and head of the water lily biorefinery in Xochimilco.

“The overabundance of the lily changes the flora, fauna, and the vocation of bodies of water. Being covered, you cannot fish, they are not navigable or recreational, ”he explains.
“Hydroelectric plants have their turbines covered. It costs money to get it out and so far no extra profit has been obtained ”.
His proposal is to make profitable those extraction costs, trying to solve the problem without generating another
How the water lily of Xochimilco is extracted
Currently, a part of the extracted water lily goes to dumps or to the soils of Xochimilco. Another stays on the banks of rivers, lakes, ponds, and dams, and causes problems due to its decomposition.

Instead, through the biorefinery it is possible to transform it into four useful products.
The first two are compost and vermicompost for soil fertilization. The third viable product is a spill absorbent that is produced by dehydration of the lily and its reduction in mills. It is used in meat traces, soft drinks, soap industries, and oil spills.
The fourth product, says Ernesto Favela Torres, is biogas. All the lily that could be contaminated becomes biofuel to generate energy and thus supply communities that do not have access to electricity.
The UAM project uses it to supply its own biorefinery, which currently processes one and a half tonnes of water lily a week with zero-waste.

“We call the plant that we have ‘the showcase’, because we want people to go and see it and build others, small or large, it does not matter, to make this project economically profitable and with a significant environmental impact,” he adds.

The biorefinery is located in the Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas Ambientales de Cuemanco, belonging to the UAM, where, in addition to working with the water lily, strategies are carried out for the conservation of the axolotl, endemic to Xochimilco.
Source: chilango.com